Using Attractors to Understand Complex Systems
▉ 05 Jan 2024 ▉ Duygu DağdelenRecently, I stumbled upon an intriguing concept known as attractors, which originates from the study of dynamical systems and chaos theory. They provide a way to understand the behavior of various systems over time. If you think about it, the world around us is made up of countless complex systems, each one interacting and influencing the others in ways that we may not always fully understand. From natural systems to the social systems of our societies, these systems are constantly in motion and constantly changing. Understanding the concept of attractors can help us gain insights into the behavior of these systems. In this post, we will explore what attractors are, how they are used to model complex systems, and how they can be used in our datasets.
What are Attractors?
An attractor offers a lens through which we can explore the dynamics of complex systems as it describes the long-term behavior of a system. Attractors are certain points, states, or regions within a dynamic system that possess the ability to draw or ‘attract’ nearby points over time. It represents a set of values or states toward which a system tends to evolve over time, regardless of its initial conditions.
They help us understand the behavior of chaotic and nonlinear systems with complex behavior by revealing underlying patterns and shedding light on the system’s stability. This allows us to predict where things might end up or what patterns they might follow, even when they’re complex and seem unpredictable.
By using attractors, we can explore the intricate web of interactions and influences that shape our world. There are different types of attractors that can be observed in datasets, depending on the nature of the data. Some common types of attractors include point attractors (single stable points), limit cycle attractors (repetitive patterns), and strange attractors (complex, non-repetitive patterns).
Because attractors represent stable patterns in time towards which a system is drawn, they help identify the underlying patterns and structures in a system’s dynamics, even when the system exhibits nonlinear or chaotic behavior. This can manifest as specific patterns, cycles, or even chaotic trajectories within the data of complex systems. By analyzing the attractors and their stability, we can explore the transitions between different attractors and the emergence of complex patterns.
Modeling Complexity with Attractors
Complexity is essentially a multitude of overlapping, dynamic influences that are bound by context and time, leading to different outcomes depending on the specific conditions. It is precisely due to this web of interconnected layers that makes complex systems challenging to predict and control.
This complexity might seem overwhelming, but this is where attractors become invaluable. They provide stable and predictable patterns within complex systems, which supports the understanding and modeling of dynamic behaviors. Attractors serve as islands of stability amidst the sea of chaos. Although chaotic and unstable by nature, dynamic complex systems tend to settle into one of several possible steady states, known as “attractor basins.”
By inducing transitions between these attractor basins, it is possible to exert some control and guide the system towards desired states. While attractors may seem like a small detail in the larger study of complex systems, they are, in fact, a fascinating concept that underpins our understanding and influence of these systems.
Attractors offer glimpses into the behavior of systems, allowing us to gain a deeper understanding of their complexities. As a result, they play a vital role in modeling complex systems, such as physics simulations involving the motion of particles in a fluid and computer graphics, to create realistic movement and behavior of particles or objects. Attractors can also be used to model more abstract systems, such as the dynamics of economic or social systems. For instance, they can help us understand the behavior of populations in a city or the spread of information through a network.
Visualizing the Influence of Parameter Changes on Attractors
Fascinated by this concept, I began to further explore attractors by visualizing distance-based attractor fields, with inspiration from a tool I had come across. Those acting as the ‘attractors’ in the field can be represented as points that exert a force of attraction on nearby objects. The strength of this attraction depends on the distance between the object and the attractor point, with closer objects experiencing a stronger pull. Objects move and interact in response to the collective influence of all the attractors in the system, creating patterns and movements that can be analyzed and understood.
Below are a few examples of my creations, showcasing the concept of attractors. I generated multiple outputs, by experimenting with the system’s parameters and applying aesthetic efforts to emphasize the attractor dynamics.
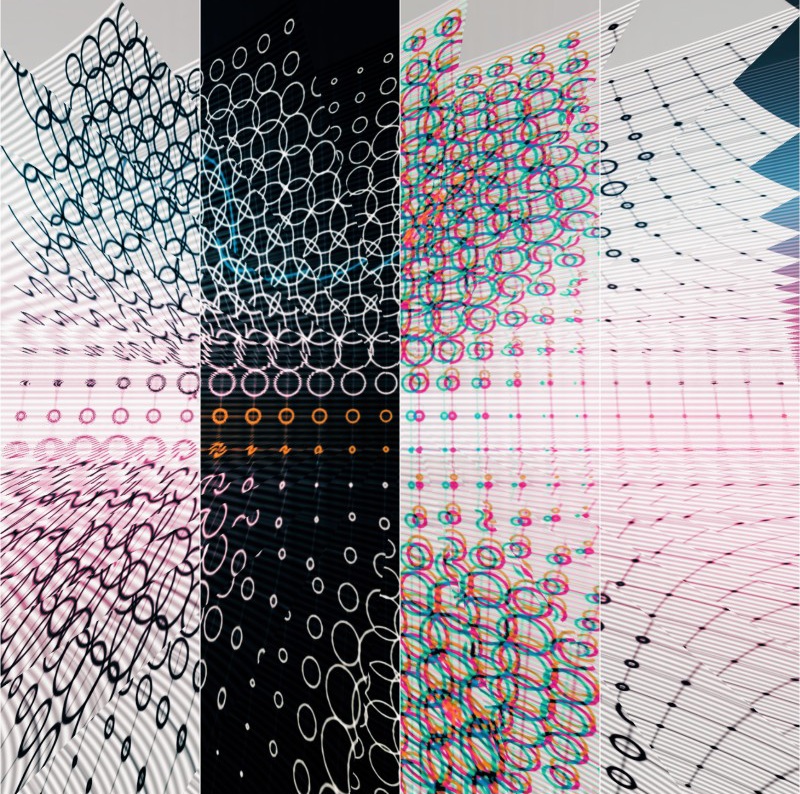
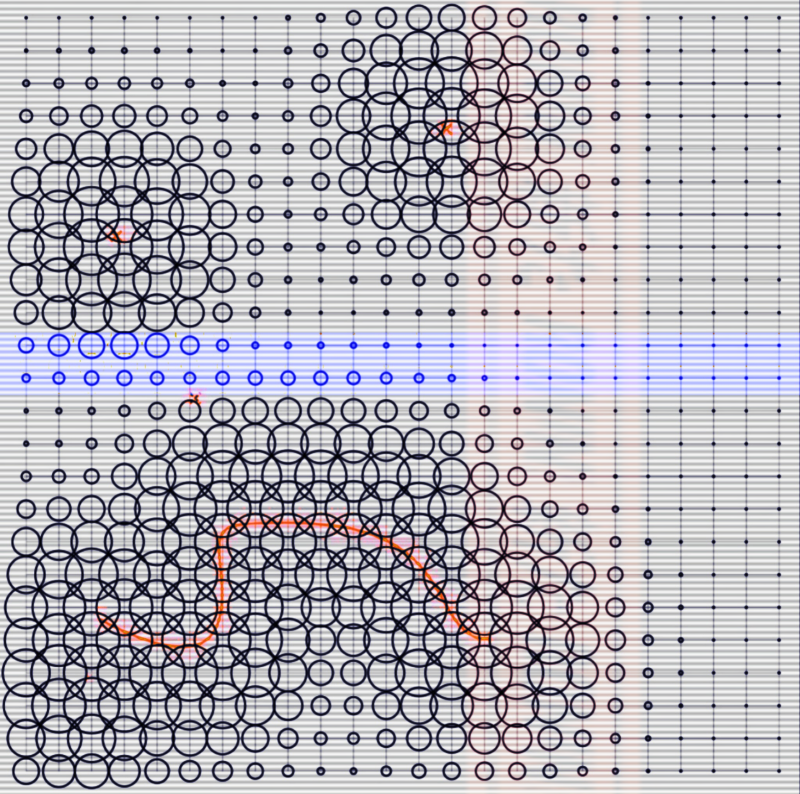

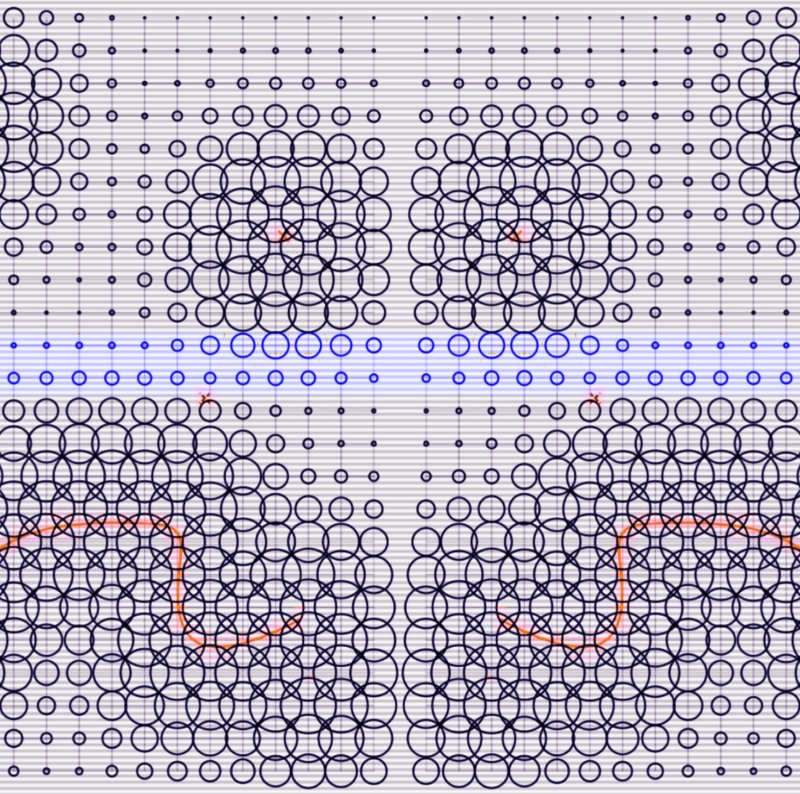
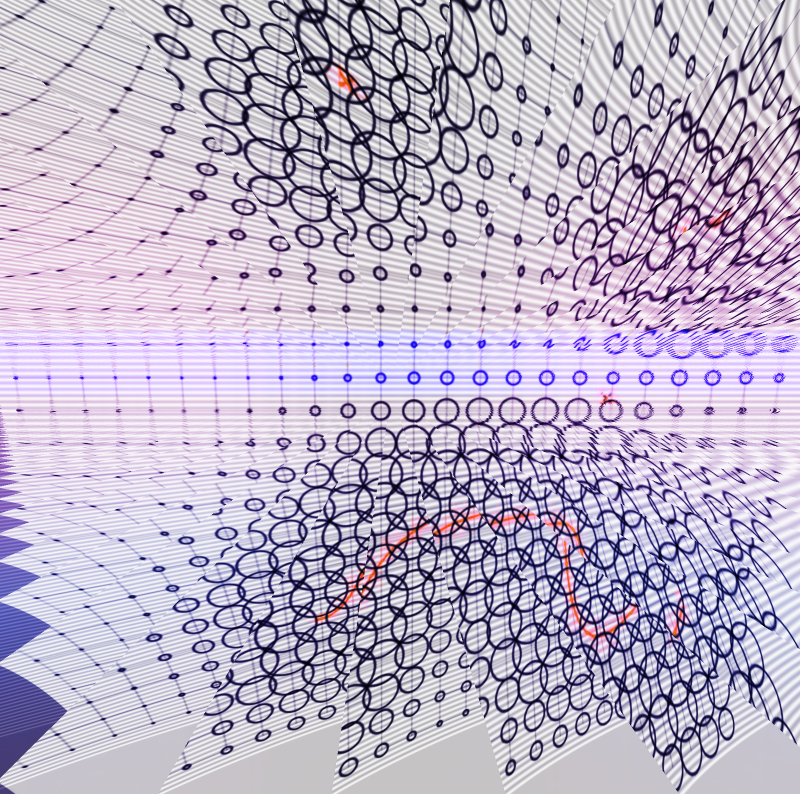
<------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------> To visualize the distance-based attractors, I used a grid of points. For each point in the grid, a value is generated based on the distance to the closest attractor. While each point is solely influenced by its closest attractor, the definition can be easily adapted to incorporate influence from multiple attractors simultaneously. The output of this definition is a single value for each point on the grid, which can then be used to control any property. In this case, it controls the radii of circles positioned on the points. <------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------>
Modifying the parameters of a dynamical system can have several effects. It can lead to the creation or elimination of attractors, shift the position or alter the shape of existing attractors. The basins of attraction associated with these attractors can change in size, shape, and location. Parameters can also influence the stability of the system, potentially converting stable regions into unstable ones and vice versa. Overall, modifying parameters has the potential to significantly influence the long-term trajectories and dynamics of a system, as well as the sets of initial conditions that lead to specific attractors. By altering parameters, we can explore how changes in the system’s dynamics impact the basins of attraction and ultimately understand how different parameter settings affect the system’s behavior. Understanding the sensitivity of the system to parameter variations is crucial for analyzing and predicting the dynamics of complex systems.
In conclusion, attractors are a powerful tool for understanding complex systems. They offer stable patterns within chaos and practical insights into various fields. Key takeaways include:
- Attractors are mathematical constructs that describe how complex systems behave over time.
- They provide stability and predictability within complex systems, aiding our understanding and control.
- Visualizing attractor fields can aid in understanding parameter changes and their effects on complex systems.
By understanding attractors, we gain a deeper appreciation for the structured and predictable aspects of the seemingly chaotic world around us
Attractors provide a valuable framework for analyzing and understanding complex systems, and visualizing them can help make sense of complex datasets, especially those with a high number of dynamic and time-series data. Thereby helping us understand how seemingly random events and patterns in complex systems can actually be structured and predictable. By understanding attractors, we can navigate the intricacies of complex systems and gain valuable insights into the interconnectedness of our world.
